- Location : Home» Newsroom
Revealing the impact mechanism of seed coating agents on the microenvironment of cotton seeds and rhizosphere soil
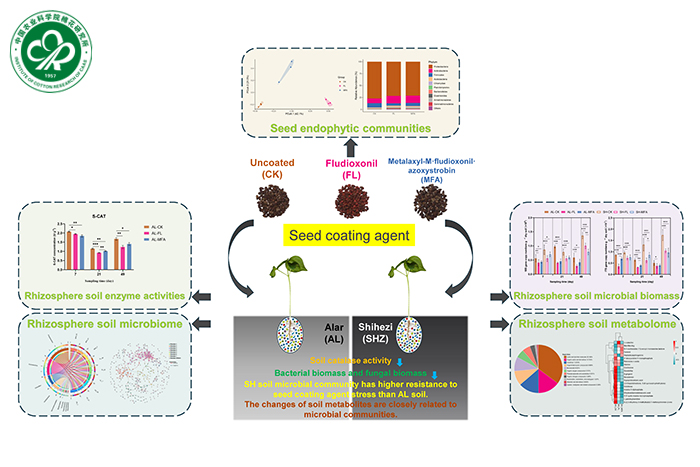
Recently, a research entitled “Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal responses ofcotton rhizosphere microbiome and metabolite spectrum to conventionalseed coating agents” has been published byEnvironmental Pollution. In this paper, Institute of Cotton Research (CCRI) researchers conducted a study on the mechanism of the impact of fungicide coating on the microenvironment of cotton seeds and rhizosphere soil through a combination of microbiological and metabolomic techniques, it was found that seed coating changed the microbial community and metabolic spectrum composition of seeds and rhizosphere soil, reduced catalase activity and total microbial biomass in rhizosphere soil, and provided theoretical basis and technical support for the rational use and improvement of seed coating agents.
This study aimed to assess the effects of fludioxonil (FL) and metalaxyl-M⋅fludioxonil⋅azoxystrobin (MFA) on cotton seed endophytes,rhizosphere soil enzymatic activities, microbiome and metabolites. Both seed coating agents significantlychanged seed endophytic bacterial and fungal communities. Growing coated seeds in the soils originating fromthe Alar (AL) and Shihezi (SH) region inhibited soil catalase activity and decreased both bacterial and fungalbiomass. Seed coating agents increased rhizosphere bacterial alpha diversity for the first 21 days but decreasedfungal alpha diversity after day 21 in the AL soil. Seed coating reduced the abundance of a number of beneficialmicroorganisms but enriched some potential pollutant-degrading microorganisms. Seed coating agents may haveaffected the complexity of the co-occurrence network of the microbiome in the AL soil, reducing connectivity,opposite to what was observed in the SH soil. MFA had more pronounced effects on soil metabolic activities thanFL. Furthermore, there were strong links between soil microbial communities, metabolites and enzymatic activities.
This study was funded by the National Key R&D Plan(2022YFD1400300) andthe National Natural ScienceFoundation of China (31901938).Researcher Feng Weiiscorresponding author,graduated Master's degree Zheng Ma and researcherHongjie Fengare the co-first authors.
The article can be found: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122058