- Location : Home» Newsroom
The strigolactone-gibberellin crosstalk mediated by a distant silencer fine-tunes plant height in upland cotton
Recently, the research entitled “The strigolactone-gibberellin crosstalk mediated by a distant silencer fine-tunes plant height in upland cotton” has been published by Molecular Plant (average IF in 5 years = 21.4). Researchers He Shoupu and Du Xiongming of the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences identified the major locus (PH 1) controlling the plant height of upland cotton, and systematically analyzed its unique molecular regulation mechanism, providing a new idea for the genetic improvement of cotton plant type.
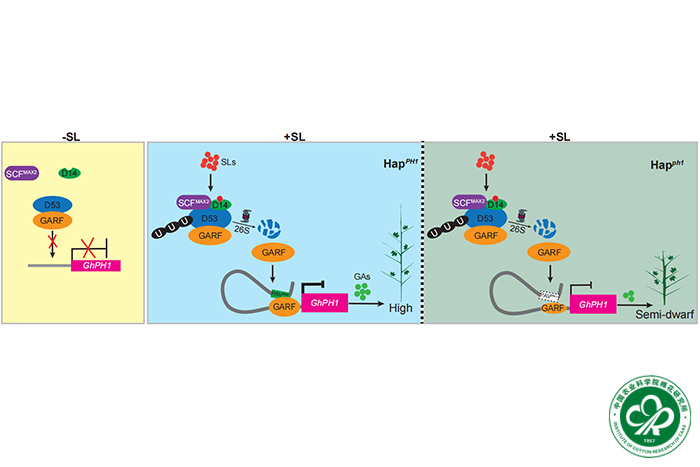
In this study, They conducted a genome-wide association study to identify a major locus controlling plant height ( PH1 ) in upland cotton. This locus encodes gibberellin 2-oxidase 1A ( GhPH1 ) and features a 1133-bp structural variation (PAV PH1 ) located approximately 16 kb upstream. The presence or absence of PAV PH1 influences the expression of GhPH1 , thereby affecting plant height. Further analysis revealed that a gibberellin-regulating transcription factor (GhGARF) recognizes and binds to a specific CATTTG motif in both the GhPH1 promoter and PAV PH1 . This interaction downregulates GhPH1 , indicating that PAV PH1 functions as a distant upstream silencer. Intriguingly, we found that DWARF53 (D53), a key repressor of the strigolactone (SL) signaling pathway, directly interacts with GhGARF to inhibit its binding to targets. Moreover, we identified a previously unrecognized gibberellin-SL crosstalk mechanism mediated by the GhD53-GhGARF- GhPH1 /PAV PH1 module, which is crucial for regulating plant height in upland cotton. These findings shed light on the genetic basis and gene interaction network underlying plant height, providing valuable insights for the development of semi-dwarf cotton varieties through precise modulation of GhPH1 expression.
This work was funded by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant nos. 2021YFF1000101 to S.H. and 2022YFD1200300 to X.D.); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32122062 to S.H.); and the Agricultural Science, Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology research project (grant no. 232102111076).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2024.08.007