- Location : Home» Newsroom
Cotton transposon-related variome reveals roles of transposon-related variations in modern cotton cultivation
Recently, a team led by Researcher Song Guoli from the Cotton Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences constructed a transposon variation map for the genus Gossypium, revealing the significant role of transposon activity in the modern cotton breeding process. The related research findings were published in the Journal of Advanced Research (IF=11.4, Q1 in multidisciplinary disciplines) under the title "Cotton transposon-related variome reveals roles of transposon-related variations in modern cotton cultivation."
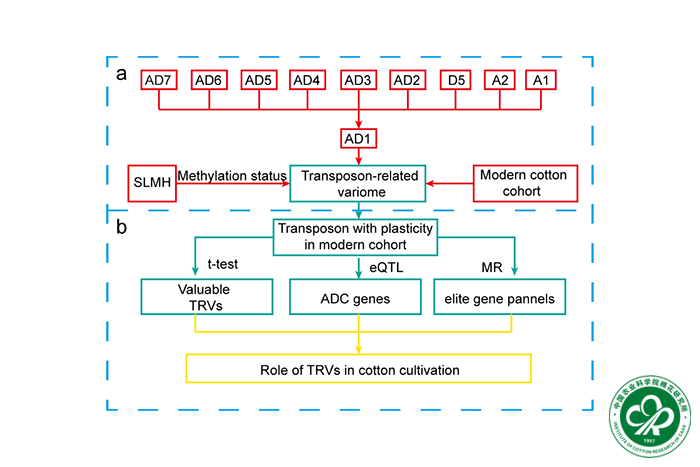
Overview of this study. Cotton’s transposon-related variations (TRVs) were recognized from genomic variations of 9 cotton genomes aligned to AD1′s genome. Epigenomic features of the TRVs were characterized by methylation prediction model, SLMH. We integrated TRVs into AD1′s genome to construct the cotton graphical transposon-related variome, and this variome was used to genotype the modern cotton cohort to identify valuable TRVs in modern cotton cultivation.Based on the plastic TRVs, we combined t-test, eQTL and MR analysis to dissect elite TRVs and genes for molecular breeding. All the findings in this study provide insights for role of transposon in modern cotton cultivation.
China Agriculture Research System (NO.CARS-15-06). Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (232300421041 and 222300420382). Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (No. 1610162022016) and Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. The funders had no role in the design of the study, collection, analysis or interpretation of the data, the writing of the manuscript or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. We thank Jikun Song for providing cotton accessions 111 and 113 for us.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2024.05.019