- Location : Home» Newsroom
Physiological and transcriptional analyses reveal formation of memory under recurring drought stresses in seedlings of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)
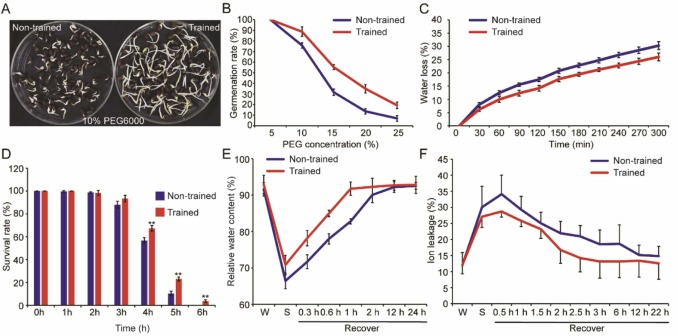
Plants are frequently subjected to a range of environmental stresses, including drought, salinity, cold, pathogens, and herbivore attacks. To survive in such conditions, plants have evolved a novel adaptive mechanism known as 'stress memory'. The formation of stress memories necessitates coordinated responses at the cellular, genetic/ genomic, and epigenetic levels, involving altered physiological responses, gene activation, hyper-induction and chromatin modification. Cotton (Gossypium spp.) is an important economic crop with numerous applications and high economic value. In this study, we establish G. hirsutum drought memory following cycles of mild drought and re-watering treatments and analyzed memory gene expression patterns. Our findings reveal the physiological, biochemical, and molecular mechanisms underlying drought stress memory formation in G. hirsutum. Specifically, H3K4me3, a histone modification, plays a crucial role in regulating [+ /+ ] transcriptional memory. Moreover, we investigated the intergenerational inheritance of drought stress memory in G. hirsutum. Collectively, our data provides theoretical guidance for cotton breeding.
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060466); the National Key Technology R&D Program, the Ministry of Science and Technology (2021YFF1000101-1). We are also acknowledged the National mid-term gene bank for cotton for providing experimental seeds.