- Location : Home» Newsroom
Insights into genetic diversity and functional significance of the bHLH genes in cotton fiber development
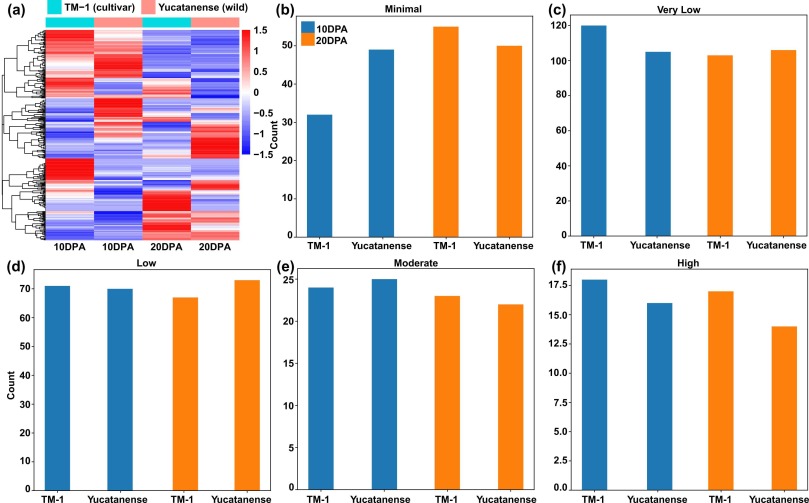
This study investigated the identification and distribution of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factors (TFs) across diverse cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) accessions, including wild, landrace, and improved varieties. Comprehensive genomic analyses revealed substantial SNP diversity in wild cotton, distinct from that observed in landraces and improved accessions. Comparative analysis showed notable variations in SNP abundance and impact levels across different accessions, with missense SNPs being prevalent. Nucleotide substitution patterns highlighted the dominance of G>A and A>G substitutions. Population genetic analyses unveiled significant genetic diversity within wild accessions and distinct clustering between wild and improved accessions. Temporal expression profiling of bHLH genes during cotton fiber development demonstrated dynamic expression patterns, emphasizing their roles in fiber initiation, elongation, and cellulose biosynthesis. Moreover, association analysis identified SNPs significantly associated within bHLH genes, particularly GhbHLH149, with fiber quality traits, indicating their potential functional significance. Population genetic analyses further revealed evidence of positive selection on GhbHLH149 during cotton improvement. This study provides a comprehensive understanding of SNP diversity, gene expression dynamics, and genetic selection in bHLH genes, offering valuable insights for future cotton breeding efforts aimed at improving fiber quality traits in cotton.
This work received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2022YFD1200304-3, No. 52161145104) and Major National R&D Projects (Grant No. 2023ZD04040-01).